The development of innovative medicine has become the most important part of drug development. In order to better guide the development of novel therapeutics, Chinese, American and European regulatory agencies have set up a variety of communication paths in the drug development process to facilitate better interaction between the sponsor and regulatory agencies to obtain timely guidance on key issues encountered in the development process.
FDA for example, the types of communication applications that are appropriate at different stages of drug development are shown in the figure below:
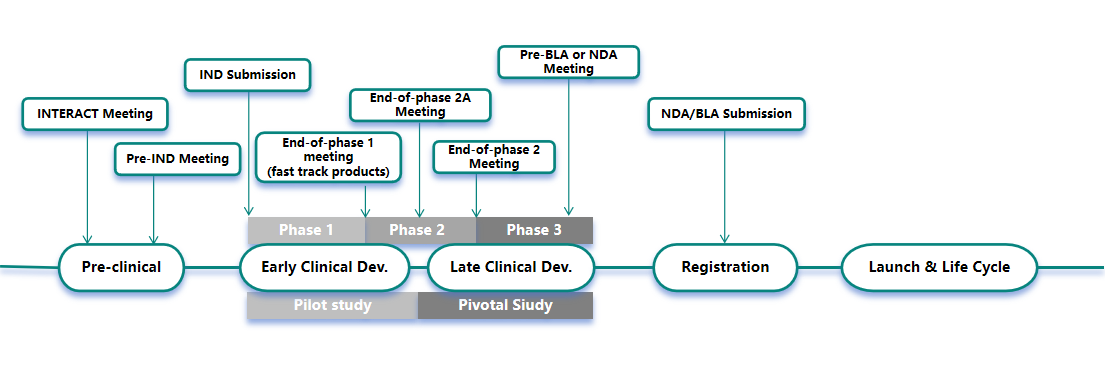
The following is an introduction to the communication and exchange of drug development and registration between China, the United States and Europe:
China
At CDE, different types of communication are set up for different stages of drug development to facilitate the technical review process. The purpose is to facilitate communication between applicants and the review team of the CDE on key technical issues not covered by current drug development and evaluation guidelines during the technical review process for drug development and registration applications.
1、Format of communications: face-to-face, video conference, teleconference or written response.
2、Meeting category:
Class I:
Meetings held to solve the major safety issues encountered in the process of clinical trials or in the case of breakthrough therapeutic drugs, in the process of research and development of major technical issues.
Meeting time: Class I meetings are generally arranged within 30 working days after the meeting request.
Class II:
Meetings held for product development in the critical phase.
Types of meetings included:
a. Pre-application meeting for clinical trials of new drugs (Pre-IND);
b. End of phase I clinical trial/end of phase II clinical trial (or before initiation)/pre-initiation of phase III clinical trial meeting (EOP1/EOP2);
c. Pre-NDA/BLA meeting (Pre-NDA/BLA);
d. Risk assessment and control meeting, and;
e. Communication meeting for application for conditional approval and/or application of priority review and approval procedures.
Meeting time: Class II meeting is generally scheduled within 60 working days after the meeting request..
Class III:
Refers to meetings other than Type I and Type II meetings.
Types of meetings included:
a. Clinical applications for new indications and new drug combinations;
b. Discussion of important policy issues such as rare disease development;
c. Discussion of significant R&D issues generics;
d. Discuss the design of complex and critical non-clinical studies;
e. Discussion of technical disagreements with Review Center;
f. Discussion of cutting-edge technologies;
g. Discussion of issues related to post-marketing changes;
h. Discussion of issues related to safety assessment and risk management during clinical trials, and;
i. Discussion of post-marketing clinical trial design.
Meeting time: Class III meetings are generally scheduled within 75 working days after application.
The above meetings set up by CDE will not incur any official fees.
The European Union
Consultation meetings in the European Union include Scientific Advice (SA) or Protocol Assistance (PA) and Pre-Marketing Authorization Application (Pre-MAA) meetings.
The Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CMPH) provides applicants with a series of communications based on different recommendation of the Scientific Advisory Working Group (SAWG) for different products at different stages of development. The applicant can apply to the EMA for an SA or PA at any stage of the drug development process, whether at the beginning of the development process or after the approval of the drug for marketing.
The usual application stage for an applicant during drug development is to apply for communication before clinical trials (pre-CTA), after Phase I clinical trials (EOP1), after obtaining Phase II clinical trial data (EOP2) and before the MAA. Communication can help the sponsor or developer to assess the adequacy of the study.
If the EMA does not raise significant objections or concerns regarding the study, it may accelerate the marketing authorization of the drug, however, if the EMA raises substantial objections, it could potentially delay the product's approval process.
SA Meeting Profile:
Purpose of the SA meeting: to provide scientific advice on specific issues in the development of innovative medicines for the sponsor.
Issues covered in the SA meeting: pharmacological, pharmacotoxicological, clinical, statistical, overall development strategy, orphan drug designation, and development programs for pediatric indications.
SA meeting time: The Scientific Advice Working Party (SAWP) holds regular monthly meetings to address applicants' questions and the EMA annually releases the scheduled meeting dates for the Scientific Advice Group therefore applicants are required to submit their meeting requests promptly in line with the published dates.
SA Meeting Costs: EMA charges a fee for scientific advice, which varies according to the scope of the advice, and currently ranges from €51,800 for single discipline to €103,800 for multiple discipline discussions.
The United States
The setup of consultation meetings between the U.S. FDA and the Chinese CDE is very similar, but there are some differences in meeting categorization and expected outcome. The FDA provides sponsors with guidance and opportunities to address questions during the innovative drug development process through a series of routine formal meetings. The types of communication meetings include type A, type B, type B (EOP) and type C meetings.
1、Format of communications: face-to-face meetings, video conferences, teleconferences or written responses.
2、Meeting category:
Type A:
For the resumption of development projects that have been suspended in the process of innovative drug development, or to solve important security problems encountered in the current drug development stage.
Types of meetings included:
a.Problem and objection resolution meetings as referenced in 21 CFR 10.75, 312.48, and 314.103;
b.Meetings to discuss clinical suspensions in drug development for a variety of reasons, and with a view to discussing new directions for development that could solve existing problems;
c. Special clinical protocol evaluation meetings requested by the sponsor, generally upon receipt of FDA's evaluation under the Special Clinical Protocol Evaluation process;
d. Post-action meetings requested within 3 months of a regulatory action (other than an approval) by the FDA;
e. A meeting requested within 30 days of the FDA refuse to file letter.
Meeting Time limit: FDA meetings are scheduled within 30 calendar days of receipt of the application.
Type B:
Related to major milestones in the product development program or process.
Types of meetings included:
a.Pre-IND meetings;
b.Pre-EUA meeting;
c. Meetings to review the Integrated Efficacy Summary (ISE) and Integrated Safety Summary (ISS);
d. Post-action meetings required 3 months after FDA regulatory action (other than approval);
e. Meetings outside the scope of marketing application review for product risk assessment and response strategies or post-market requirements;
f. Meetings to discuss the overall development plan for a product certified as a breakthrough therapy.
Meeting Time limit: Pre-IND FDA response time 21 calendar days, FDA meeting scheduled within 60 calendar days of receipt of application; Pre-NDA/BLA response time 14 calendar days, FDA meeting scheduled within 70 calendar days of receipt of application.
Category B (EOP) Meeting:
A meeting held after the completion of a specific phase in the drug development process and prior to preparing to move to the next phase.
Types of meetings included:
a.End of Phase I Clinical Trials (EOP1) for biologics for the treatment of life-threatening and severely debilitating diseases and drugs that have received accelerated approval and are intended for use in serious/life-threatening conditions;
b.EOP2/3.
Meeting Time limit: 14 calendar days for response time and 70 calendar days for FDA meeting scheduling after receipt of application.
Type C Meeting:
Communication meetings that are not Class A, B, or B (EOP) meetings, for topics related to product development and review.
Types of meetings included:
a.EOP2A meetings;
b.OTC monograph feedback meetings;
c. Phase 4 meetings.
Meeting Time: 21 calendar days for FDA response time and 75 calendar days for FDA meeting scheduling after receipt of application.
Interact meeting:
Sponsors of complex therapies, novel therapeutics, advanced therapies, and novel biological products engage in informal meetings with CBER. These meetings aim to obtain non-binding advice from the FDA regarding CMC, pharmacology/toxicology, and/or clinical development plans.
CBER gains insights through these early interactions to understand that the development of such innovative products may present unique challenges. These challenges could be related to unknown safety issues, complex manufacturing processes, technical problems, innovative devices, and the use of cutting-edge testing methods.
Meeting Time: FDA response time is 21 calendar days, and FDA meetings are scheduled within 90 calendar days of receipt of the request.
No fees will incur for all above meetings set by the FDA.
Overall, the types of communication and meeting setups for drug development and registration between CDE and FDA are highly similar. Apart from the INTERACT meeting uniquely established by the FDA and differences in meeting timelines, the overall meeting structures are largely consistent.
In contrast, the communication and meeting setup for EMA is relatively simpler in terms of categories but covers a broader range of content. It essentially includes all aspects addressed in the communication meetings between China and the U.S., with fees adjusted based on the scope and depth of the communication required.
As an internationalized enterprise with 20 years of experience in the field of clinical CRO, SDM Bioservice has a professional regulatory team in China, which is well versed in the global drug regulations and in line with the international frontiers. SDM Bioservice has successfully assisted domestic and foreign customers in completing the registration of a number of therapeutic drugs, vaccines, and medical devices and enabled these clients for the pharmaceutical innovations to go global. We are looking forward to joining hands with more partners.
Contact SDM regulatory team at any time!
This session focuses on Stakeholder Engagement: developing strategies for collaborative project decision-making and execution.
The updated draft guidance involves a focus on clinical trial design, regulatory considerations, and whether these trials can demonstrate that the drugs can maintain weight loss as determined by BMI.
Let's take a look back at the previous two installments of the Clinical Data Management “PM” series: Scope Management, which clarifies the scope of responsibilities of all parties involved in a clinical trial, and Project Resource Management, which focuses on the utilization of company and personal resources to accomplish data management tasks. In this installment, we will focus on the most important part of project management - project schedule management - to share the timeline planning and progress follow-up of data management activities, so as to efficiently complete the data management work under the premise of ensuring the data quality and reaching the important milestones of the project.
In the last session, we learned about project scope management for data management work, identifying the scope of responsibilities for data cleansing and data management activities. After defining the scope of the data management work, in this session, we will learn how to mobilize the resources within the scope of work to carry out the data management work more efficiently and with higher quality.
Shanghai SDM Vaccine Data Management Department, in collaboration with the International Project Department, has launched a series of training sessions on "Application of Project Management Knowledge in Data Management." The Application of Project Management Knowledge in Data Management Work contains eight modules, including Project Integration Management, Project Scope Management, Project Progress Management, Project Quality Management, Project Resource Management, Project Communication Management, Project Risk Management, and Project Stakeholder Management, etc. It mainly refers to the theoretical knowledge of the Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK Guide) and combines the content of the data management work and practical experience of the project.
Want to quickly penetrate the Chinese, American and European pharmaceutical markets? Registering for communication exchanges is the key!
SDM PV team detects drug safety risks.
SDM Vaccine Experts Share Roadmap to Avoid Clinical Trial Pitfalls.
this article outlines essential documentation preparation and strategic considerations for conducting pre-IND communication meetings with CDE, ensuring effective regulatory alignment and adequate guidance.
Global Vaccine Solutions via Multidimensional Strategies.
July 23, 2025 GSK disclosed that the FDA has postponed PDUFA date of the Blenrep® (belantamab mafodotin) combination therapy BLA. The agency established a new action date of October 23, 2025 for completion of BLA review.
SDM Bioservices has successfully established a hybrid immuno-capture LC-MS/MS platform for the simultaneous quantification of ADC total antibody, conjugated antibody, conjugated drug, and free small-molecule payload. This approach significantly reduces reliance on specific antibody reagents, enables rapid method development and validation, and supports high-throughput sample analysis—thereby accelerating project timelines and advancing drug development efforts.
Premier Li Qiang has signed a State Council decree, promulgating the "Regulations on the Administration of Clinical Research and Translation of Novel Biomedical Technologies." This important regulation was adopted at the State Council executive meeting on September 12, 2025, and will take effect on May 1, 2026. This establishes a comprehensive legal framework for China's oversight of novel biomedical technologies throughout the entire chain from research to application.
Get in touch with SDM experts for your questions or comments and a member of our team will get back to you directly.
Let's Start a Conversation