Data Management spans the entire clinical trial lifecycle, requiring Data Managers to apply project management knowledge for planning, executing, monitoring, and quality controlling of daily data-related tasks.
Shanghai SDM Vaccine Data Management Department, in collaboration with the International Project Department, has launched a series of training sessions on "Application of Project Management Knowledge in Data Management." The Application of Project Management Knowledge in Data Management Work contains eight modules, including Project Integration Management, Project Scope Management, Project Progress Management, Project Quality Management, Project Resource Management, Project Communication Management, Project Risk Management, and Project Stakeholder Management, etc. It mainly refers to the theoretical knowledge of the Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK Guide) and combines the content of the data management work and practical experience of the project.

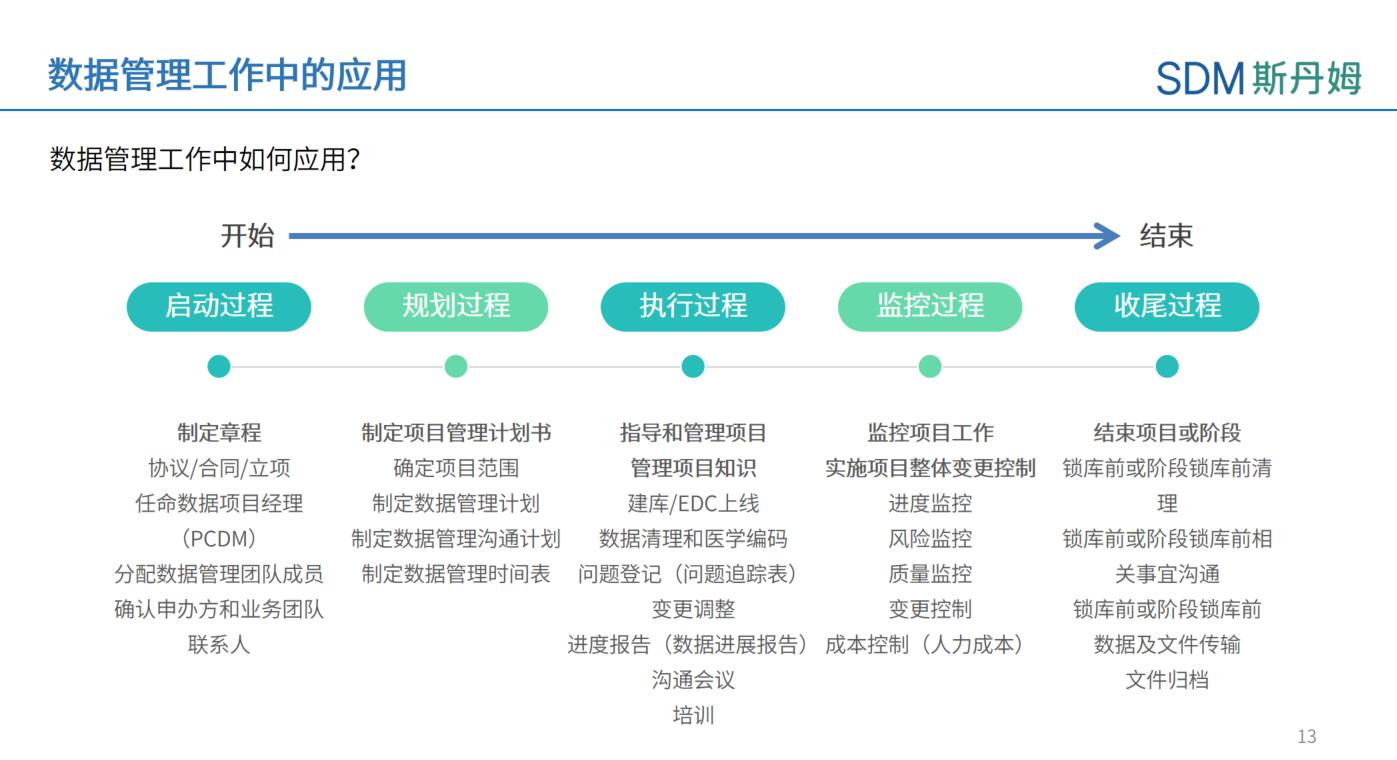
Basics of project management knowledge in data management
The Principal Clinical Data Manager (PCDM) is a role similar to that of a PM in data management, and is required to plan End to End data management related work throughout the entire clinical trial cycle.In the planning stage, the Principal Data Manager has to set up a team, confirm the relevant parties, plan the timeline for database construction, monitor the health status of the project data throughout the trial, assess the risks, hold regular meetings with the relevant parties to discuss and solve the data problems, and do a good job in the quality management of the data documentation, EDC, and data cleansing.To summarize, a good data manager is one who can plan and execute data management work from the aspects of time schedule, project risk, communication with related parties and quality control.

Project scope management
Let's start by understanding what project scope management is. Project scope management involves the processes of ensuring that the project does and only does all the work required to successfully complete the project. Managing project scope is mainly about defining and controlling what work should be included in the project and what should not to [1]. So there are three main points we need to think about when it comes to good scope management: what are the other side's needs? What do we need to do? How do we do it? The application of project scope management in data management work has two main parts: the division of responsibilities for data management activities and the division of the scope of data verification.
RACI principle for data management activities
The process of clinical trial data management often involves multiple tasks and multiple personnel. In order to better manage the work, the main data manager in the initial phase of the project should know the people involved in each data management activity and their responsibilities, so it is necessary to develop the corresponding RACI, where R - who is responsible, A - who is accountable, C - who is consulted, and I - who is informed. The RACI defines the responsibilities and attributes of activities and people in the initiation, implementation, and completion phases of a data management effort. The following figure shows a sample RACI diagram for a data management effort:
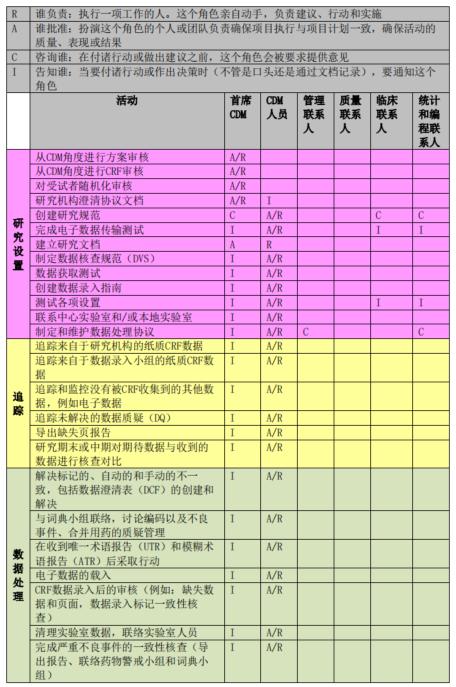
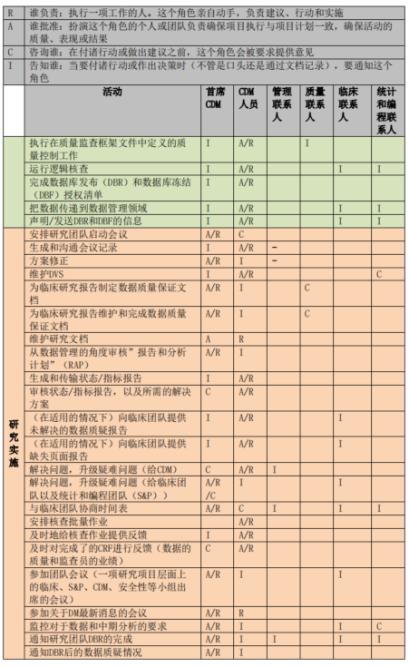
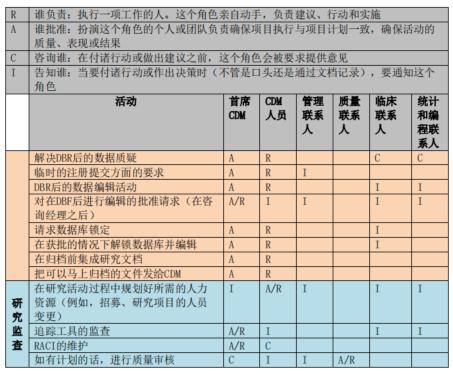
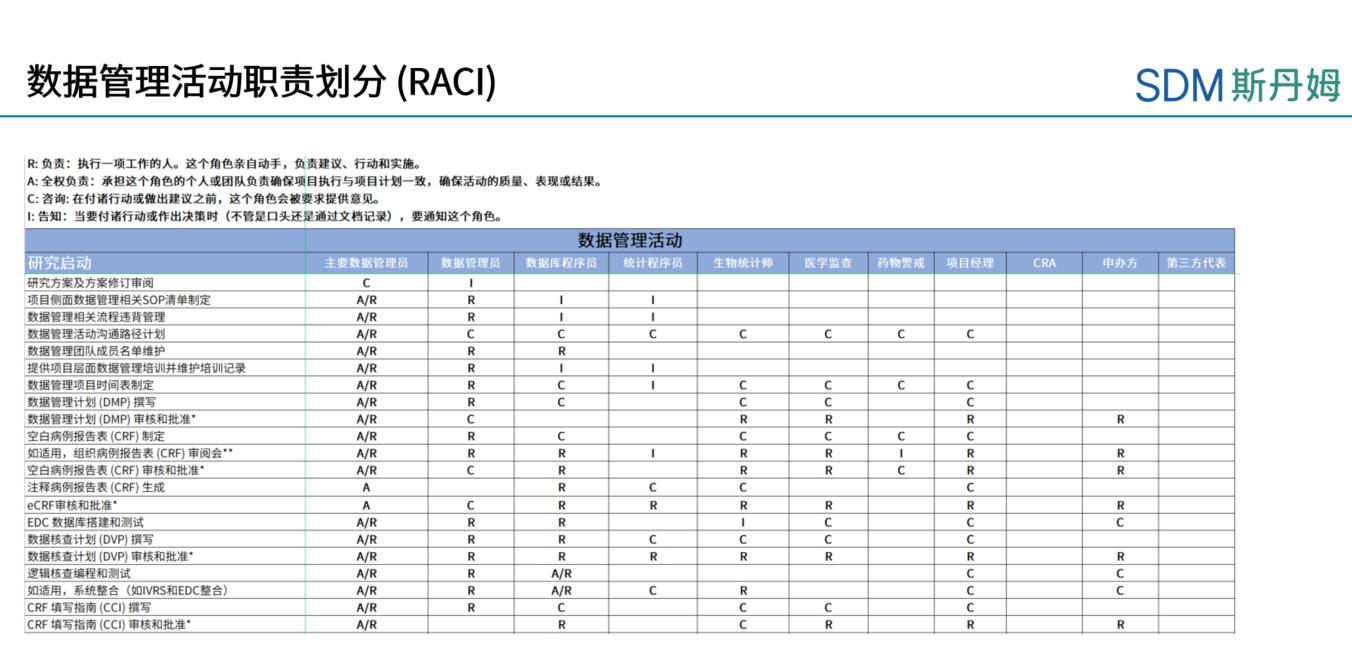
Shanghai SDM Vaccine Data Management Department RACI Legend
Once the project is underway, the Lead Data staff should perform each data management activity according to the RACI and consult or inform the relevant parties. If the RACI defines A or R, the appropriate role performs and is accountable for document review and approval, system testing and feedback; if the RACI defines C or I, the Lead Data Steward consults with or informs the relevant parties when reviewing or approving documents. All relevant parties also need to review the RACI in advance to clarify their responsibilities.
At the same time, within the data management team, the responsibilities of each member should be clearly defined, such as the Primary Data Manager, Clinical Data Manager, Database Designer, SAS Programmer, Coder, and Non-Blind Data Manager, and the scope of work and the way of cooperation between them should be clarified. Clarify the scope of work and cooperation among the parties.
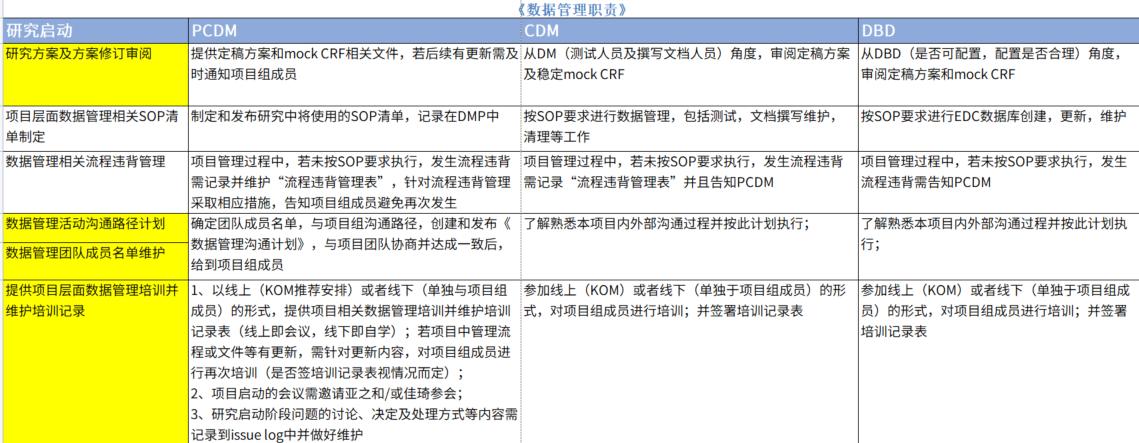
Shanghai SDM Vaccine Data Management DepartmentLegend
As clinical trials are complex and varied, one may also encounter problems that are not defined in advance during the project no matter how detailed the document description is. let's take account management as an example.
Problem statement:
Project XXX has no docking between IRT system and EDC system due to the tight start-up time. Some time after the system was launched, the data administrator accidentally found that several personnel applied for non-blind pharmacist accounts in the IRT system, but applied for blind CRA accounts in the EDC system, and had already started to do SDV and send CRA query in EDC. The data administrator quickly reported this to the project team, and since the non-blind personnel could no longer carry out the operations related to the blind roles, the project team decided to Deactivate the blind account of the above personnel. To prevent this type of incident from happening again, should the data manager perform quality control on the EDC and IRT account information every time an account request is received?
Suggestion:
According to the Guiding Principles for Blinding of Drug Clinical Trials, based on the blinding method determined by the clinical trial, each study participant should refine the division of responsibilities and be divided into blinded and unblinded maintenance personnel according to the authorization requirements of his position. Strict measures should be taken to set up a "firewall" between blinded and unblinded personnel to avoid accidental blinding [3].
The IRT and EDC systems should have a complete set of rights management settings, including role settings, workflow settings, and granting of permissions, etc., and the data team needs to formulate an SOP for the control and management of system rights. Different permissions are granted to different people or roles in the system, and only authorized people are allowed to operate (e.g., record, modify, etc.), and appropriate methods should be adopted to monitor and prevent the operation of unauthorized people [4]. Collecting system permissions from members of all parties during the project requires close collaboration between the PM and the data manager. It is recommended that the PM or designee (representative of each party), who understands the division of labor among the personnel of each party in the clinical trial, conducts the first account application QC at the time of account collection to confirm that the personnel roles and application privileges match the system privileges. The data manager can assist in checking whether there are inconsistencies in the permissions applied for among multiple systems after receiving the permission application form confirmed by the PM.
Data Verification Scope
The collection and cleaning of clinical trial data requires close cooperation between departments, and each department needs to review and question the data from different perspectives. The data manager carries out verification according to the Data Verification Plan, which routinely includes but is not limited to: missing value verification, eCRF page missing verification, range verification, duplicate value verification, logical consistency verification of the same eCRF page, logical consistency verification of different eCRF pages, external data verification, SAE consistency verification, protocol deviation, etc. The CRA needs to ensure that the EDC data is consistent with the original documents to ensure the accuracy and consistency of the data. The medical supervisor can verify the clinical trial data from the safety and medical perspectives, so as to protect the rights and interests of the subjects and guarantee the reliability of the clinical trial data from the medical perspectives, and at the same time, provide medical advice on the relevant steps of the clinical trial.
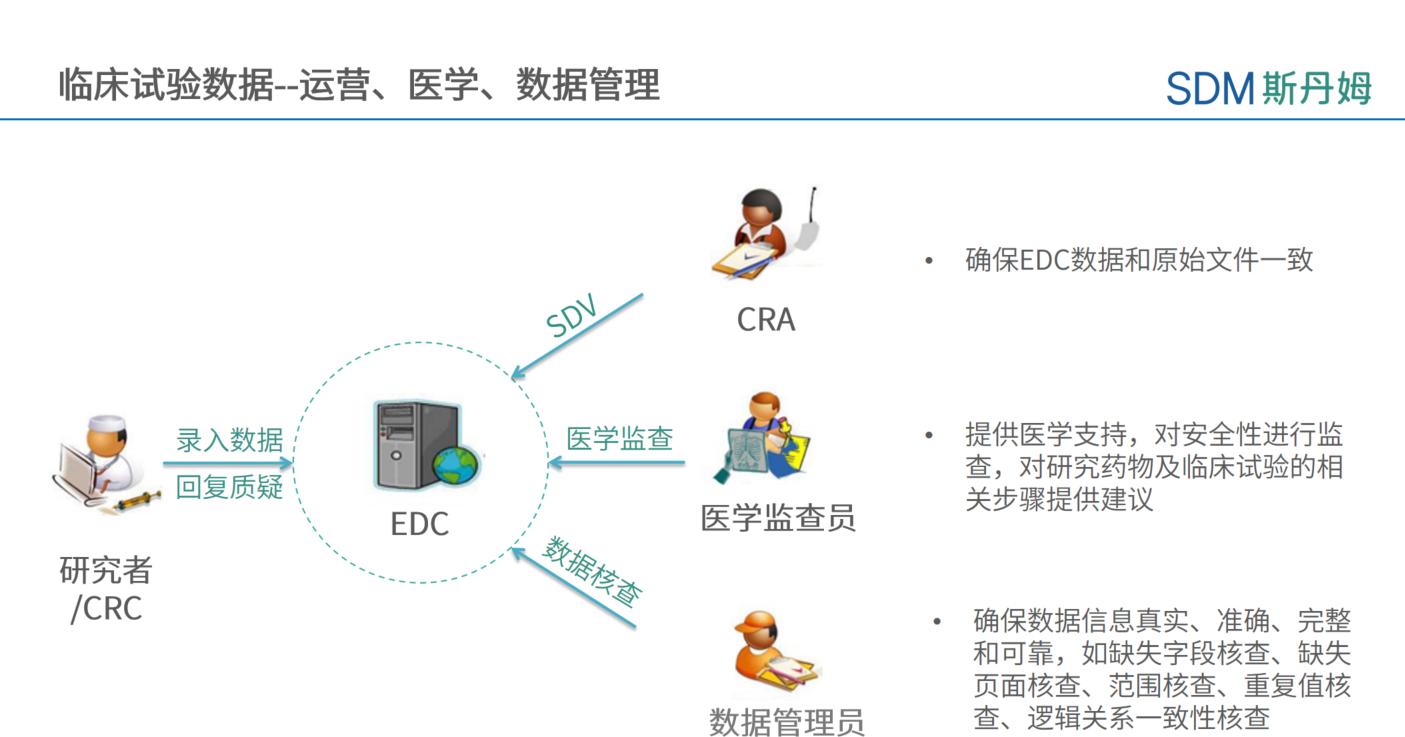
For more efficient data cleansing, an iDRP (integrated Data Review Plan) can be drafted at the company level to define the scope of medical, data, and operational tri-party verification in order to avoid missing and duplicating data points. The scope of verification can include the form in the figure below:

As an example, for the Adverse Event (AE) form, verification involving medical knowledge judgment is completed by the medical monitor, such as reasonableness determination of multiple data points: including AE association with combined drug/non-drug therapy, AE relevance determination, AE grading determination, AE name documentation, AE disposition of vaccine used in the trial; potential duplicate AEs; discontinuance of the trial's primaryAE, etc. The Data Administrator performs consistency checks for elements with fixed logic, including but not limited to: AE and study summary, time window of AE and associated concomitant drug/non-drug therapy, laboratory AEs and laboratory test results, SAE consistency, regression and end date, etc. The data manager for the vaccine program also needs to additionally conduct rationalization verification of enlistment vs. non-enlistment, vaccination site vs. non-vaccination site, vaccination dosage, and enlistment time window; rationalization of splitting the diagnosis and symptom records within the enlistment period; bi-directional verification of fever vs. AE within the enlistment period; and verification of the relevance of localized AEs vs. the test vaccine within the enlistment period, etc.

Protocol Deviation (PD) also require multi-party collaboration for collection and verification.The Operations team collects and verifies the Protocol Deviation List summarized at the program level.The Medical Monitor reviews the PDs and determines their classification. The Data Manager identifies and documents potential PDs through logical verification and sends them to the Operations Team and Medical Monitor to confirm if there are any underreported PDs. At important points in the project (mid-term analysis or final lockout), the Data Administrator should verify the Program Deviation List with the EDC data for consistency.

The clarity and delineation of project scope management allows professionals to do professional things, and project teams to do their own jobs, work closely together, and deliver better project results more efficiently.
References:
[1]: Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK® Guide), Sixth Edition
[2]: Clinical Data Quality Management Specification, October 2013 Edition
[3]: Guiding Principles for Blinding of Pharmaceutical Clinical Trials
[4]: Technical Guidelines for Clinical Trial Data Management Work
This session focuses on Stakeholder Engagement: developing strategies for collaborative project decision-making and execution.
The updated draft guidance involves a focus on clinical trial design, regulatory considerations, and whether these trials can demonstrate that the drugs can maintain weight loss as determined by BMI.
Let's take a look back at the previous two installments of the Clinical Data Management “PM” series: Scope Management, which clarifies the scope of responsibilities of all parties involved in a clinical trial, and Project Resource Management, which focuses on the utilization of company and personal resources to accomplish data management tasks. In this installment, we will focus on the most important part of project management - project schedule management - to share the timeline planning and progress follow-up of data management activities, so as to efficiently complete the data management work under the premise of ensuring the data quality and reaching the important milestones of the project.
In the last session, we learned about project scope management for data management work, identifying the scope of responsibilities for data cleansing and data management activities. After defining the scope of the data management work, in this session, we will learn how to mobilize the resources within the scope of work to carry out the data management work more efficiently and with higher quality.
Shanghai SDM Vaccine Data Management Department, in collaboration with the International Project Department, has launched a series of training sessions on "Application of Project Management Knowledge in Data Management." The Application of Project Management Knowledge in Data Management Work contains eight modules, including Project Integration Management, Project Scope Management, Project Progress Management, Project Quality Management, Project Resource Management, Project Communication Management, Project Risk Management, and Project Stakeholder Management, etc. It mainly refers to the theoretical knowledge of the Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK Guide) and combines the content of the data management work and practical experience of the project.
Want to quickly penetrate the Chinese, American and European pharmaceutical markets? Registering for communication exchanges is the key!
SDM PV team detects drug safety risks.
SDM Vaccine Experts Share Roadmap to Avoid Clinical Trial Pitfalls.
this article outlines essential documentation preparation and strategic considerations for conducting pre-IND communication meetings with CDE, ensuring effective regulatory alignment and adequate guidance.
Global Vaccine Solutions via Multidimensional Strategies.
July 23, 2025 GSK disclosed that the FDA has postponed PDUFA date of the Blenrep® (belantamab mafodotin) combination therapy BLA. The agency established a new action date of October 23, 2025 for completion of BLA review.
SDM Bioservices has successfully established a hybrid immuno-capture LC-MS/MS platform for the simultaneous quantification of ADC total antibody, conjugated antibody, conjugated drug, and free small-molecule payload. This approach significantly reduces reliance on specific antibody reagents, enables rapid method development and validation, and supports high-throughput sample analysis—thereby accelerating project timelines and advancing drug development efforts.
Premier Li Qiang has signed a State Council decree, promulgating the "Regulations on the Administration of Clinical Research and Translation of Novel Biomedical Technologies." This important regulation was adopted at the State Council executive meeting on September 12, 2025, and will take effect on May 1, 2026. This establishes a comprehensive legal framework for China's oversight of novel biomedical technologies throughout the entire chain from research to application.
Get in touch with SDM experts for your questions or comments and a member of our team will get back to you directly.
Let's Start a Conversation